Data has emerged as one of an organization’s most important assets in the current digital era. However, with the increasing reliance on technology, businesses face growing threats from cybercriminals who target sensitive information. A data breach can result in significant financial loss, reputational damage, and legal implications. According to recent studies, data breaches are becoming more frequent and costly, with the average global cost of a data breach reaching millions of dollars.
As businesses increasingly use cloud computing, remote work environments, and complex digital systems, the risk of data breaches continues to rise. Detecting the early signs of a breach can help minimize the damage and protect your organization from further loss. In this article, we’ll explore the common signs that your company might be experiencing a data breach and how to respond effectively to minimize the impact.
What is a Data Breach?
The illegal access to sensitive, private, or protected data by third parties is known as a data breach. This can include personally identifiable information (PII), intellectual property, financial records, or proprietary business information. Data breaches can happen due to various reasons, such as hacking, malware, phishing attacks, or insider threats.
While some breaches are immediately noticeable, others can go undetected for months, giving attackers more time to exploit the stolen information. This makes it crucial for businesses to understand the signs of a data breach and implement strategies for early detection.
Common Signs Your Company Might Be Experiencing a Data Breach
1. Unusual Network Activity

One of the earliest and most common signs of a data breach is unusual network activity. This could involve unexpected spikes in data traffic, unknown devices connecting to your network, or unauthorized access to servers or databases. Suspicious activity on the network might indicate that cybercriminals are attempting to move data out of your systems or that malicious software has been installed.
Red Flags:
- Unexplained data transfers or downloads.
- Increased bandwidth usage, especially during off-hours.
- Unknown devices or users accessing the network.
Regularly monitoring network traffic can help detect any irregularities that might indicate a breach, allowing you to take immediate action to prevent further damage.
2. Unexplained Changes in User Accounts
Cybercriminals often target user accounts, especially those with administrative privileges, to gain access to sensitive information. If you notice unexplained changes in user accounts, such as unauthorized password changes, unusual login locations, or accounts being locked out without reason, it could be a sign of a breach.
Red Flags:
- Accounts being locked or passwords being changed without user knowledge.
- Login attempts from unfamiliar or unexpected locations.
- Employees reporting trouble accessing their accounts.
Monitoring user activity and implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) can help prevent unauthorized access to critical systems and data.
3. Unexpected Software Installations
If your IT department notices new or unfamiliar software installed on company devices, this could be a sign of malware or a breach. Hackers often install malicious software to gain control of systems, steal data, or disrupt business operations. These programs may be hidden or disguised as legitimate software, making them difficult to detect.
Red Flags:
- Unfamiliar programs appearing on devices.
- Changes in software configurations without authorization.
- Antivirus or security software being disabled.
Ensure your organization has strong antivirus and endpoint protection systems in place, and regularly scan devices for malware or rogue software installations.
4. Suspicious Emails or Phishing Attempts
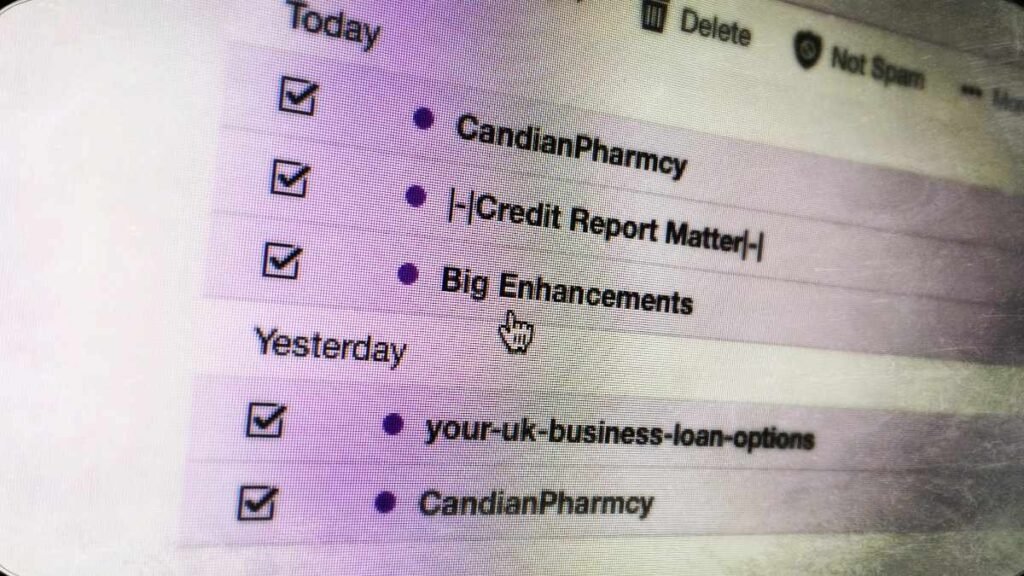
Phishing attacks remain one of the most common methods cybercriminals use to breach company data. If your employees start receiving an unusual volume of suspicious emails, especially those asking for sensitive information or containing malicious attachments, this could be a sign that your company is being targeted.
Red Flags:
- Phishing emails requesting login credentials, bank details, or other sensitive data.
- Increased reports of employees clicking on suspicious links.
- Emails from fake or compromised accounts posing as trusted contacts.
Educating employees about phishing attacks and encouraging them to report suspicious emails is essential to prevent cybercriminals from gaining access to your data.
5. Strange Behavior of Company Systems
Unexplained slowdowns, crashes, or glitches in your company’s systems might indicate that your systems have been compromised. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in your network infrastructure to install malware or disrupt normal operations. If your systems are behaving erratically, it’s essential to investigate immediately.
Red Flags:
- Computers or servers running unusually slow.
- Frequent system crashes or application failures.
- Unexplained pop-ups or system notifications.
Regularly updating and patching software can help reduce the likelihood of attackers exploiting known vulnerabilities in your systems.
6. Unauthorized Access to Sensitive Files

If sensitive files, such as financial documents, customer data, or proprietary information, are being accessed by unauthorized users, this could indicate a breach. Attackers might attempt to move or exfiltrate this data, which can have devastating consequences for your business.
Red Flags:
- Unauthorized access to files or folders that contain sensitive data.
- Changes in file permissions or access rights without explanation.
- Deleted or missing files.
Implementing access controls, encryption, and activity logging can help protect sensitive data and detect any unauthorized access before it escalates into a full-blown breach.
7. Unexplained Financial Discrepancies
Another sign of a potential data breach is financial discrepancies, such as unauthorized transactions, missing funds, or errors in financial records. Cybercriminals often target companies’ financial systems to steal money or disrupt operations.
Red Flags:
- Unexplained financial transactions or missing funds.
- Discrepancies in invoices, billing, or payroll.
- Vendors or clients reporting unauthorized payments.
Regular financial audits and the use of secure payment processing systems can help identify and prevent fraudulent activity.
8. Unusual Pop-ups or Warnings from Security Software
If your employees start seeing frequent pop-ups or warnings from your company’s security software, it could indicate that your systems are under attack. These warnings might alert you to malware, phishing attempts, or other types of cyber threats.
Red Flags:
- Security software warning about viruses or malware.
- Frequent pop-ups from firewalls or antivirus software.
- Software alerts about unauthorized access attempts.
Ensure that your security software is up to date and properly configured to detect and respond to emerging threats.
9. Third-party Vendor Compromise

A breach at one of your third-party vendors or partners can also affect your organization, especially if you share sensitive data or integrate their systems with yours. If one of your vendors reports a data breach, it’s essential to assess whether your data was compromised in the process.
Red Flags:
- A vendor reports a data breach or security incident.
- Suspicious activity or access requests from third-party systems.
- Changes in the behavior of systems that rely on vendor services.
Ensure that your third-party vendors have strong cybersecurity practices and regularly review contracts to ensure they meet your company’s security requirements.
10. Reports of Identity Theft from Customers or Employees
If your customers or employees report identity theft or fraud, it could be a sign that their personal data has been compromised in a breach. This is especially concerning for organizations that handle large amounts of personal information, such as financial institutions or healthcare providers.
Red Flags:
- Customers or employees reporting unauthorized activity on their accounts.
- Sudden complaints of identity theft or fraudulent charges.
- Increased calls or emails from individuals asking about data security concerns.
Immediate action should be taken to investigate the source of the breach and protect affected individuals by offering credit monitoring services and informing regulatory authorities.
What to Do If You Suspect a Data Breach

If you suspect that your company is experiencing a data breach, quick action is essential to minimize the damage. Here’s what you should do:
1. Contain the Breach
First, take immediate steps to contain the breach by isolating affected systems or networks. This may involve disconnecting devices from the internet or shutting down compromised servers. The goal is to stop the breach from spreading further.
2. Notify Key Personnel
Alert your IT and cybersecurity teams, as well as relevant executives, about the breach. Ensure that your incident response team is ready to take action.
3. Assess the Damage
Determine the scope of the breach by identifying what data was accessed, how the attackers gained access, and how long they were in your systems. This assessment will help guide your next steps.
4. Notify Affected Parties
If customer or employee data is compromised, you must notify them as soon as possible. Transparency is critical to maintaining trust and mitigating reputational damage.
5. Report the Breach
In many jurisdictions, data breach notification laws require businesses to report breaches to regulatory authorities. Make sure to comply with any legal obligations to avoid fines or penalties.
6. Review Security Protocols
After the breach has been contained, conduct a thorough review of your security protocols to identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities. Apply greater safety precautions to prevent future breaches.
Conclusion
Data breaches are a growing concern for businesses of all sizes, and the consequences can be severe. Understanding the early warning signs of a breach and responding quickly can help mitigate the damage. By staying vigilant, implementing robust cybersecurity practices, and fostering a culture of security awareness, your organization can protect itself against the increasing threat of cyberattacks.